In part one this series I briefly introduced the molecular workings of cannabis through terpenes & the sense of smell. Now I will discuss the fact that humans make there own cannabis endogenously or within our bodies. Read further to see what I mean.
Cannabinoids
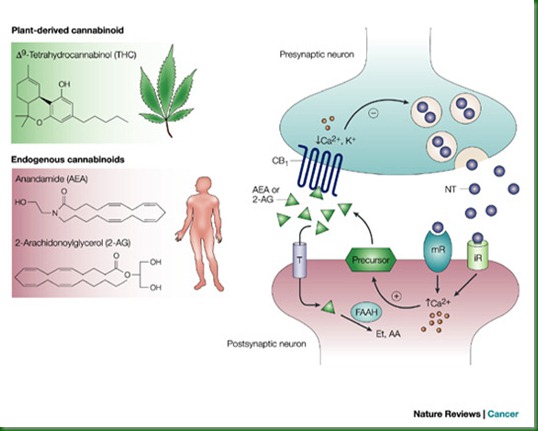
Cannabinoids or “antagonists (in the medical sense),” are molecules that activate one or both CB1/CB2 receptors. In other words, the canabinoids are message coded signals, in the form of molecules that carry a certain message for a specific receiver. Some Cannabinoids are produced through cannabis & are called photocannabinoids, while others are produced by our own bodies called endocannabinoids. A well known photocannabinoid, delta-9-tetrahhydrocannabinol or THC was first identified by Dr. Raphael Mechoulam at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem 1964.” THC can give signals of calm, anxiety, hunger, or even euphoria depending on the part of the brain/body most receptive to the signal.
Photocannabinoids
Studies have revealed more photocannabinoids as well. Cannabidiol or CBD which is the predominant cannabinoid in plants typically bred for fiber has been designated a Schedule I substance even though it has no known adverse effects or doesn't induce “euphoria.” The most dire effects of Cannabis, tachycardia (accelerated heartbeat), panic, confusion, anxiety, even psychosis, are affects of THC that CBD have been show to mitigate.
Endocannabinoids
In 1992, Dr. Mechoulam “discovered a small fatty acid produced in the brain, Arachidonic Acid Ethanolamine (AEA) an endocannadoid which he named anandamide after the Sanskrit word ananda, meaning bliss;” that binds to the CB1receptor & mimics all the activities of Cannabis. Another endocannabinoid would shortly be discovered by Daniele Piomelli & Nephi Stella of the University of California at Irvine named 2-arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG), which is even more abundant in certain brain regions than anandamide (AEA) is. We all have different congenital endocanabinoid levels & sensitivities.
Cannabinoid Receptors
Cannabinoid Receptors are small proteins embedded in the membranes of all cells, including neurons, & when specific molecules bind to them-fitting like one puzzle piece into another, changes in the cell occur. Cannabinoid Receptors function as subtle sensing devices, tiny vibrating scanners perpetually primed to pick up biochemical cues that flow through fluids surrounding each cell. Some receptors have water-filled spores or channels that permit chemical ions to pass into or out of the cell. Canabinoid Receptors are not channels, but are coupled to specialized proteins called G-proteins. These G-protein-coupled receptors represent a large family that set in motion a variety of biochemical signaling cascades within cells, often resulting in changes in ion channels.
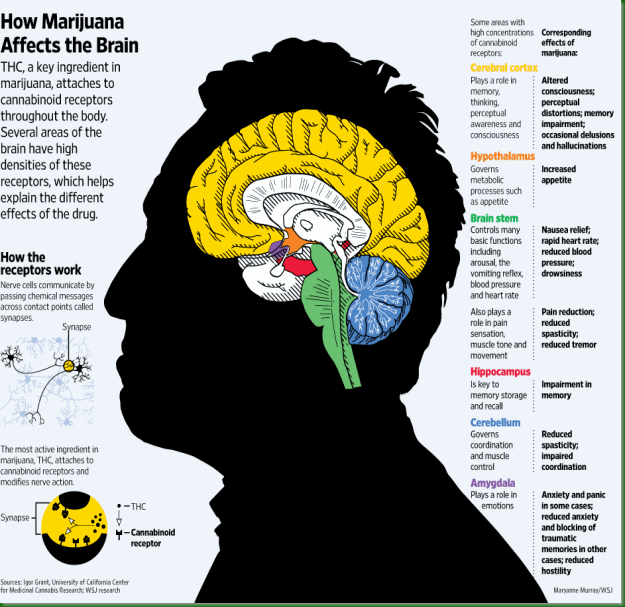
One of the most abundant G-protein coupled receptor CB1 is located in the brain. It has its highest densities in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, hypothalamus, cerebellum, basal ganglia, brain stem, spinal cord & amygdala. This distribution explains Cannabis' diverse effects. Its psychoactive power comes from its action in the cerebral cortex. Memory impairment is rooted in the hippocampus, a structure essential for memory formation. Motor dysfunction is cause by acting on movement control centers in the brain. In the brain stem & spinal cord, it brings about the reduction of pain; the brain stem also controls the vomiting reflex. The hypothalamus is involved in appetite, the amygdala in emotional responses.

No comments:
Post a Comment